| [1]Urita Y,Komuro H,Chen G,et al.Evaluation of diaphragmatic hernia repair using PLGA mesh-collagen sponge hybrid scaffold: an experimental study in a rat model.Pediatr Surg Int.2008;24(9):1041-1045. [2]Jung Y,Park MS,Lee JW,et al.Cartilage regeneration with highly-elastic three-dimensional scaffolds prepared from biodegradable poly(L-lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone). Biomaterials.2008;29(35):4630-4636. [3]Aravind A,Nair R,Raveendran S,et al.Aptamer conjugated paclitaxel and magnetic fluid loaded fluorescently tagged PLGA nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy.J Magn Magn Mater.2013;344(344):116-123.[4]Jagani HV,Josyula VR,Palanimuthu VR,et al.Improvement of therapeutic efficacy of PLGA nanoformulation of siRNA targeting anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 through chitosan coating.Eur J Pharm Sci.2013;48(4-5):611-668.[5]Cui Y,Xu Q,Chow PK,et al.Transferrin-conjugated magnetic silica PLGA nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin and paclitaxel for brain glioma treatment.Biomaterials. 2013; 34(33):8511-8520.[6]Lin L,Gao H,Dong Y.Bone regeneration using afreeze-dried 3D gradient-structured scaffold incor-porating OIC-A006-oaded PLGA microspheresbased on beta-TCP/PLGA. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2015;26(1):5327.[7]林利,王伟莉,黄继锋,等.彩色多普勒超声对PRGD复合神经导管修复周围神经缺损的评价[J].华南国防医学杂志, 2014,(6): 570-572.[8]门永芝,於子卫.生物材料构建神经导管修复周围神经损伤的研究进展[J].听力学及言语疾病杂志,2014,22(6):654-658.[9]王华松,吴刚,黄继锋,等.新型仿生人工神经导管修复周围神经缺损的初步临床观察[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2014,32(6): 735-738.[10]Jeon S,Jha MK,Ock J,et al. Role of lipocalin-2-chemokineaxis in the development of neuropathic pain followingperipheral nerve injury.J Biol Chem.2013;288(33):24116-24127.[11]Arslantunali D,Budak G,Hasirci V.Multiwalled CNT-pHEMAcomposite conduit for peripheral nerve repair.J Biomed MaterRes A.2014;102(3):828-841.[12]Benzina O,Szabo V,Lucas O,et al.Changes induced byperipheral nerve injury in the morphology and nanomechanicsof sensory neurons.J Biomed Opt.2013; 18(10):106014.[13]Huang J,Zhang Y,Lu L,et al.Electrical stimulationaccelerates nerve regeneration and functional recovery indelayed peripheral nerve injury in rats.Eur J Neurosci.2013; 38(12): 3691-3701.[14]张伟,岳靓,易红蕾,等.自组装多肽凝胶联合可降解神经导管修复长节段周围神经损伤[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(24): 2083-2087.[15]刘勇,侯春林.神经导管研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2010, 31(5): 279-221.[16]赵文.新型复合材料神经导管促进周围神经再生的研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2007.[17]张伟,侯春林.神经移植术修复周围神经损伤[J].国外医学(骨科学分册),2002,23(2):98-101.[18]Hsieh SC,Tang CM,Huang WT,et al.Comparison between twodifferent methods of immobilizing NGF in poly(DL-lacticacid-co-glycolic acid) conduit for peripheral nerveregeneration by EDC/NHS/MES and genipin.J Biomed MaterRes A.2011;99A(4):576-585.[19]段永畅,田广永,郑伟,等.载NGF海藻酸凝胶-聚乳酸复合导管修复兔面神经缺损实验研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2014,32(2): 189-191.[20]张伟才,黄继锋,严琼娇,等.PNGF导管复合骨髓间充质干细胞修复大鼠12 mm坐骨神经缺损[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2014, 32(3):325-329.[21]Gao Z,Luo X,Li N,et al.Application of Amniotic ExtracellularMatrix Nerve Conduit with Biological Material in the Peripheral Nerve Defect in vivo.Adv Mater Res.2011; 322:173-176.[22]Nakajima Y,Nishiura Y,Hara Y,et al.Simultaneous graduallengthening of proximal and distal nerve stumps for repair ofchronic peripheral nerve defect in rats.Hand Surg. 2012;17(1):1-11.[23]钱婷玉,崔爱军,彭松,等.聚乳酸-羟基乙酸(PLGA)及其载药微球的制备研究[J].化工新型材料,2015,43(12):143-145.[24]Qi R,Guo R,Zheng F,et al.Controlled release and antibacterial activity of antibiotic-loaded electrospun halloysite/ poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)composite nanofibers.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2013;110:148-155.[25]郭立强.高分子量聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物的合成[J].牡丹江师范学院学报(自然科学版),2014,87(2):13-15.[26]Shin KC,Kim BS,Kim JH,et al.A facileprepration of highly interconnected macroporous PL GA scaf2folds by liquid2liquid phase separation. Polymer.2005;(46):3801-3808.[27]Shen H,Hu X,Yang F,et al. Combining oxygen plasma treatment with anchorage of cationized gelatin for enhancing cell affinity of poly(lactide-co-glycolide).Biomaterials. 2007; 28(29):4219-4230.[28]Zhang ZJ,Li YJ,Liu XG,et al.Human umbilical cord blood stem cells and brain-derived neurotrophic factor for optic nerve injury: a biomechanical evaluation.Neural Regen Res.2015; 10(7):1134-1138.[29]Wang Y,Li ZW,Luo M,et al.Biological conduits combining bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular matrix to treat long-segment sciatic nerve defects.Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(6):965-971.[30]张勇杰,金岩,聂鑫,等.组织工程周围神经修复坐骨神经缺损应用研究[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2004,3(2):141-144.[31]汪玉海,金丽娟,高俊,等.脂肪干细胞复合PLGA 对骨质疏松骨折愈合后生物力学的影响[J].宁夏医科大学学报, 2013,3(3): 244-247.[32]Kim WS,Vacanti JP,Cima L,et al. Cartilage engineered in predetermined shapes employing cell transplantation on synthetic biodegradable polymers.Plast Reeonstr Surg.1994; 94(2):233.[33]李正伟,常笑语,李新颖,等.模拟坐骨神经损伤以聚乳酸-羟基乙酸管移植修复后蠕变特性的分析[J].生物医学工程研究,2015, 34(3):178-181. [34]Peng SW,Li CW,Chiu IM,et al.Nerve guidance conduit with a hybrid structure of a PLGA microfibrous bundle wrapped in a micro/nanostructured membrane.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017; 12:421-432. [35]Aldayel AM,Naguib YW,O'Mary HL,et al.Acid-Sensitive Sheddable PEGylated PLGA Nanoparticles Increase the Delivery of TNF-α siRNA in Chronic Inflammation Sites.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.2016;5:e340. [36]Bonaccorso A,Musumeci T,Carbone C,et al.Revisiting the role of sucrose in PLGA-PEG nanocarrier for potential intranasal delivery.Pharm Dev Technol. 2017:1-34. doi: 10.1080/10837450.2017.1287731. [Epub ahead of print][37]Liu X,Baldursdottir SG,Aho J,et al.Electrospinnability of Poly Lactic-co-glycolic Acid (PLGA): the Role of Solvent Type and Solvent Composition.Pharm Res. 2017. doi: 10.1007/s11095-017-2100-z. [Epub ahead of print][38]Landau S,Szklanny AA,Yeo GC,et al.Tropoelastin coated PLLA-PLGA scaffolds promote vascular network formation.Biomaterials.2017;122:72-82. [39]Ni R,Muenster U,Zhao J,et al.Exploring polyvinylpyrrolidone in the engineering of large porous PLGA microparticles via single emulsion method with tunable sustained release in the lung: In vitro and in vivo characterization.J Control Release. 2017;249:11-22. [40]Abamor ES.Antileishmanial activities of caffeic acid phenethyl ester loaded PLGA nanoparticles against Leishmania infantum promastigotes and amastigotes in vitro.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017;10(1):25-34. |
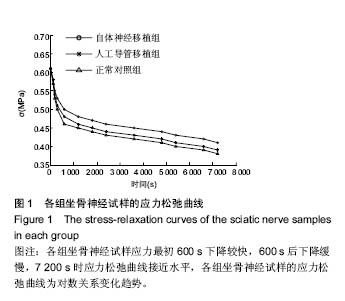
.jpg)
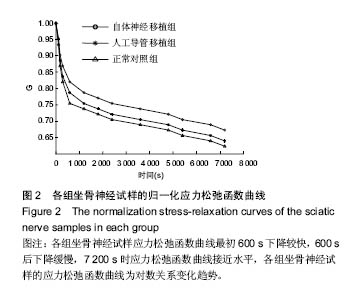
.jpg)
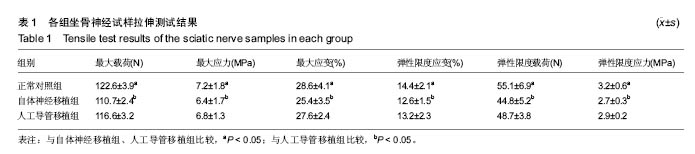
.jpg)
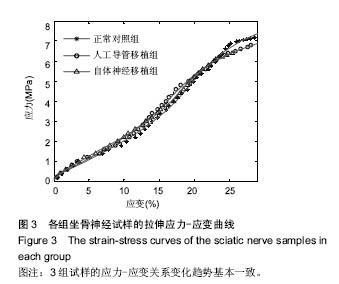
.jpg)